| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Mo | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.78 - 0.88 | 0.20 - 0.45 | 0.15 - 0.40 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 3.75 - 4.50 | 4.50 - 5.50 | 1.75 - 2.20 |
Virat Special Steels is the largest Supplier & Stockiest of M2 in India.
M2 is a standard high-speed steel grade. Having balanced alloy composition forms the basis of its high toughness and good cutting edge retention, rendering it suitable for a large variety of applications.
This grade is mainly used for all metal-cutting tools for roughing or finishing such as twist drills, diverse milling cutters, thread dies, broaches, reamers, countersinks, thread chasers, circular saw segments, shaping tools and woodworking tools. Also highly suitable for cold-forming tools such as cold extrusion rams and dies, as well as cutting and precision cutting tools, plastic moulds with elevated wear resistance and screws.
A general-purpose high-speed steel of the molybdenum type, M2 steel has balanced toughness, wear-resistance, and red hardness characteristics. This grade is frequently used in cold work punches, dies, and high-speed, light-cutting applications. Due to its better qualities, such as its bending strength, toughness, and thermo-plasticity, all of which are 50% greater than T1, M2 High Speed steel is by far the most often used high-speed steel in place of T1 in most applications. Group M steels make up over 95% of the high-speed steels produced in the US.
Except for M6, all varieties of steel from M1 through M10 contain tungsten, and none of these steels contain cobalt. Tools constructed of this type of steel can be coated with titanium nitride, titanium carbide, and several other materials using a physical vapor deposition technique to increase their functionality and durability.
Virat Special Steels is the largest stockiest and supplier of M2 Steel in flat, square and round bar. We provide steel in all sizes as your requirements. M2 die steel is available in flat, square and round shape. Consult our team who will assist you for M2 steel query.
Standard high-speed steel grade. Its well-balanced alloy composition forms the basis of its high toughness and good cutting edge retention, rendering it suitable for a large variety of applications.
| Tensile strength | 1000-1400 MPa |
| Yield Strength | 3250 MPa |
| Abrasion (loss as-hardened; ASTM G65) | 25.8 mm3 |
| Impact Toughness | 67 J/cm2 |
| Hardness | 262 HRC |
| Modulus of elasticity | 207 GPa |
These physical properties are approximate values and can vary depending on the specific composition , heat treatment and manufacturing processes used for M2 steel.
| Thermal Conductivity at °C | 20 | 350 | 700 |
| W/(m*K) | 32.8 | 23.5 | 25.5 |
M2/DIN 3343/AISI M2 High Speed steels are rapidly heated from 2610°C (4730°F) to 3960°C (7160°F) after being preheated at 2610°C (4730°F) before hardening. These steels are then quenched in air, a salt bath, or oil after cooling for 3 to 5 minutes. The following details are offered solely as a guide. Due to the form, size, and other external parameters of each component, the rate of heating, cooling, and soaking durations will vary.
The M2/DIN 3343/AISI M2 should be preheated twice, at 450–500°C and 850–900°C, respectively. Heat the material further until it achieves a final hardening temperature of 1200–1250°C. Don't leave the steel at the temperature of hardening for too long. until it reaches 500°C, quench in hot oil or brine, then air cool to room temperature.
Quenching mediums are heated oil, pressurized gas, or salt. To attain the necessary characteristics for pressurized gas, a quick quench rate to below 1000°F (538°C) is essential. For oil, quench at 900°F (482°C) or until it becomes black, then cool to 150–125°F (66–51°C) in calm air. Equalise, then cool in calm air to 150-125°F (66-51°C) for salt that is kept at 1000-1100°F (538-593°C).
Temper immediately after quenching. A tempering range of 1025–1050°F (552–566°C) is typical. Hold at temperature for two hours before air-cooling to ambient. Dual tempering is necessary. Triple tempering is strongly advised for large cross sections, particularly for blanks from which wire EDM tools will be machined.
Preheat gently to between 850 and 900°C, then immediately raise the temperature to between 1050 and 1150°C for forging. Forge at 880–900°C or higher. After forging, cool extremely gently.
A double preheat is used to reduce distortion and stress in large or complex equipment. Heat the component to 1450-1550°F (788-843°C) at a steady rate. Then cool in the air.
After heat working and before re-hardening, annealing is required. Heat at a rate not to exceed 400°F (222°C) per hour to 1525–1550°F (829–843°C), and maintain the desired temperature for a minimum of two hours for every inch (25.4 mm) of thickness. After that, use the furnace to gradually cool at a pace not to exceed 50°F (28°C) every hour up to 1000°F (538°C). In the air or the furnace, keep cooling until the desired temperature is reached
M2/DIN 3343/AISI M2 should not be normalized.
A sealed chamber with a regulated nitrogen-rich environment, usually ammonia gas (NH3), is used to store M2/DIN 3343/AISI M2 steel. The chamber is heated for a prolonged length of time, ranging from 20 to 100 hours, to a particular temperature between 500 and 600 degrees Celsius. Nitrogen atoms penetrate into the steel's surface during this period, generating nitride compounds that enhance the material's surface characteristics.
Set the component's temperature to 1100°F (600°C) and keep it there throughout welding. After that, let the components cool gently.
| Soft annealing °C | Cooling | Hardness HB |
|---|---|---|
| 770 - 860 | Furnace | max. 269 |
| Stress-relief annealing °C | Cooling |
|---|---|
| 630 - 650 | Furnace |
| 1st pre-heating °C | 2nd and 3rd | Hardening °C | Quenching | Tempering °C | Hardness after Teperature HRC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| up to approx. 400 in an air-circulating furnace | 850 and 1050 | 1190 - 1230 | Saltbath, at least 550 °C Oil ,Air | at least twice 530-560 | 64 – 66 |
For cold-forming tools with a complex geometry, a hardening temperature at the lower end of the quoted range is recommended. The stated hardening temperatures apply to saltbath hardening only. For vacuum hardening, we suggest a reduction of 10 °C to 30 °C.
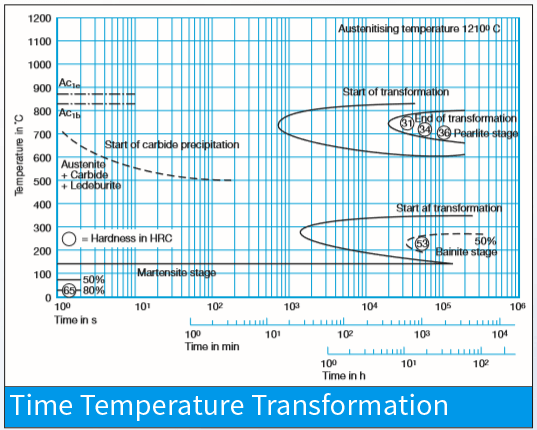
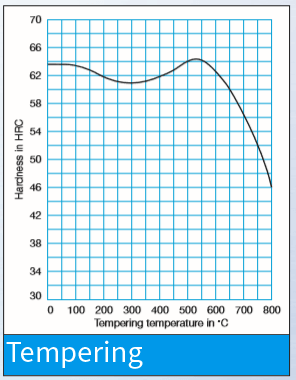
For all metal-cutting tools for roughing or finishing such as twist drills, diverse milling cutters, thread dies, broaches, reamers, countersinks, thread chasers, circular saw segments, shaping tools and woodworking tools. Also highly suitable for cold-forming tools such as cold extrusion rams and dies, as well as cutting and precision cutting tools, plastic moulds with elevated wear resistance and screws.